부스팅 방법#
부스트(boost) 방법은 미리 정해진 갯수의 모형 집합을 사용하는 것이 아니라 하나의 모형에서 시작하여 모형 집합에 포함할 개별 모형을 하나씩 추가한다. 모형의 집합은 위원회(commitee) \(C\)라고 하고 \(m\)개의 모형을 포함하는 위원회를 \(C_m\)으로 표시한다. 위원회에 들어가는 개별 모형을 약 분류기(weak classifier)라고 하며 \(k\)로 표시한다.
부스트 방법의 특징은 한번에 하나씩 모형을 추가한다는 것이다.
그리고 \(m\)번째로 위원회에 추가할 개별 모형 \(k_m\)의 선택 기준은 그 전단계의 위원회 \(C_{m-1}\)의 성능을 보완하는 것이다.
위원회 \(C_m\)의 최종 결정은 다수결 방법을 사용하지 않고 각각의 개별 모형의 출력을 가중치 \(\alpha\)로 가중선형조합한 값을 판별 함수로 사용한다. 또한 부스트 방법은 이진 분류에만 사용할 수 있으며 \(y\)값은 1또는 -1의 값을 가진다.
에이다부스트#
에이다부스트(adaboost)라는 이름은 적응 부스트(adaptive boost)라는 용어에서 나왔다. 에이다부스트는 위원회에 넣을 개별 모형 \(k_m\)을 선별하는 방법으로는 학습 데이터 집합의 \(i\)번째 데이터에 가중치 \(w_i\)를 주고 분류 모형이 틀리게 예측한 데이터의 가중치를 합한 값을 손실함수 \(L\)로 사용한다. 이 손실함수를 최소화하는 모형이 \(k_m\)으로 선택된다.
위 식에서 \(I\)는 \(k(x_i) \neq y_i\)라는 조건이 만족되면 1, 아니면 0을 가지는 지시함수(indicator function)이다. 따라서 틀린 문제에 대한 가중치의 합이다.
위원회 \(C_m\)에 포함될 개별 모형 \(k_m\)이 선택된 후에는 가중치 \(\alpha_m\)를 결정해야 한다. 이 값은 다음처럼 계산한다.
데이터에 대한 가중치 \(w_{m,i}\)는 최초에는(m=1)모든 데이터에 대해 같은 값을 가지지만 위원회가 증가하면서 값이 바뀐다. 가중치의 값은 지수함수를 사용하여 위원회 \(C_{m-1}\)이 맞춘 문제는 작게, 틀린 문제는 크게 확대(boosting)된다.
\(m\)번째 멤버의 모든 후보에 대해 위 손실 함수를 적용하여 가장 값이 작은 후보를 \(m\)번째 멤버로 선정한다.
에이다부스팅은 사실 다음과 같은 손실함수를 최소화하는 \(C_m\)을 찾아가는 방법이라는 것을 증명할 수 있다.
개별 멤버 \(k_m\)과 위원회의 관계는
이고 이 식을 대입하면
\(y_i\)와 \(k_M(x_i)\)가 1 또는 -1값만 가질 수 있다는 점을 이용하면,
\(L_m\)을 최소화하려면 \(\sum_{i=1}^N w_{m,i} I\left(k_m(x_i) \neq y_i\right)\)을 최소화하는 \(k_m\) 함수를 찾은 다음 \(L_m\)을 최소화하는 \(\alpha_m\)을 찾아야 한다.
이 조건으로부터 \(\alpha_m\) 공식을 유도할 수 있다.
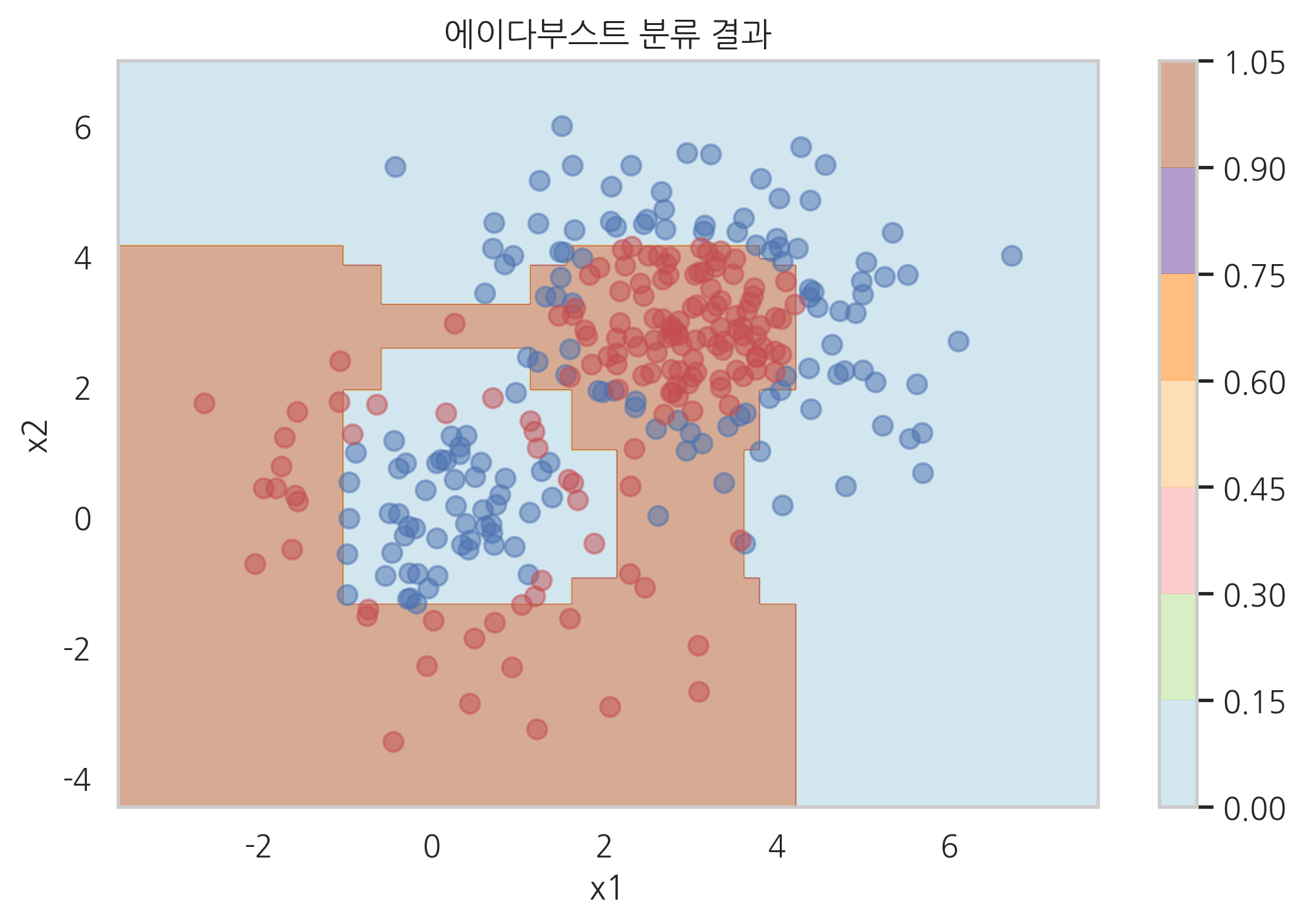
다음은 scikit-learn의 ensemble 서브패키지가 제공하는 AdaBoostClassifier 클래스를 사용하여 분류 예측을 하는 예이다. 약분류기로는 깊이가 1인 단순한 의사결정나무를 채택하였다.
여기에서는 각 표본 데이터의 가중치 값을 알아보기 위해 기존의 AdaBoostClassifier 클래스를 서브클래싱하여 가중치를 속성으로 저장하도록 수정한 모형을 사용하였다.
from sklearn.datasets import make_gaussian_quantiles
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
X1, y1 = make_gaussian_quantiles(cov=2.,
n_samples=100, n_features=2,
n_classes=2, random_state=1)
X2, y2 = make_gaussian_quantiles(mean=(3, 3), cov=1.5,
n_samples=200, n_features=2,
n_classes=2, random_state=1)
X = np.concatenate((X1, X2))
y = np.concatenate((y1, - y2 + 1))
class MyAdaBoostClassifier(AdaBoostClassifier):
def __init__(self,
base_estimator=None,
n_estimators=50,
learning_rate=1.,
algorithm='SAMME.R',
random_state=None):
super(MyAdaBoostClassifier, self).__init__(
base_estimator=base_estimator,
n_estimators=n_estimators,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
random_state=random_state)
self.sample_weight = [None] * n_estimators
def _boost(self, iboost, X, y, sample_weight, random_state):
sample_weight, estimator_weight, estimator_error = \
super(MyAdaBoostClassifier, self)._boost(iboost, X, y, sample_weight, random_state)
self.sample_weight[iboost] = sample_weight.copy()
return sample_weight, estimator_weight, estimator_error
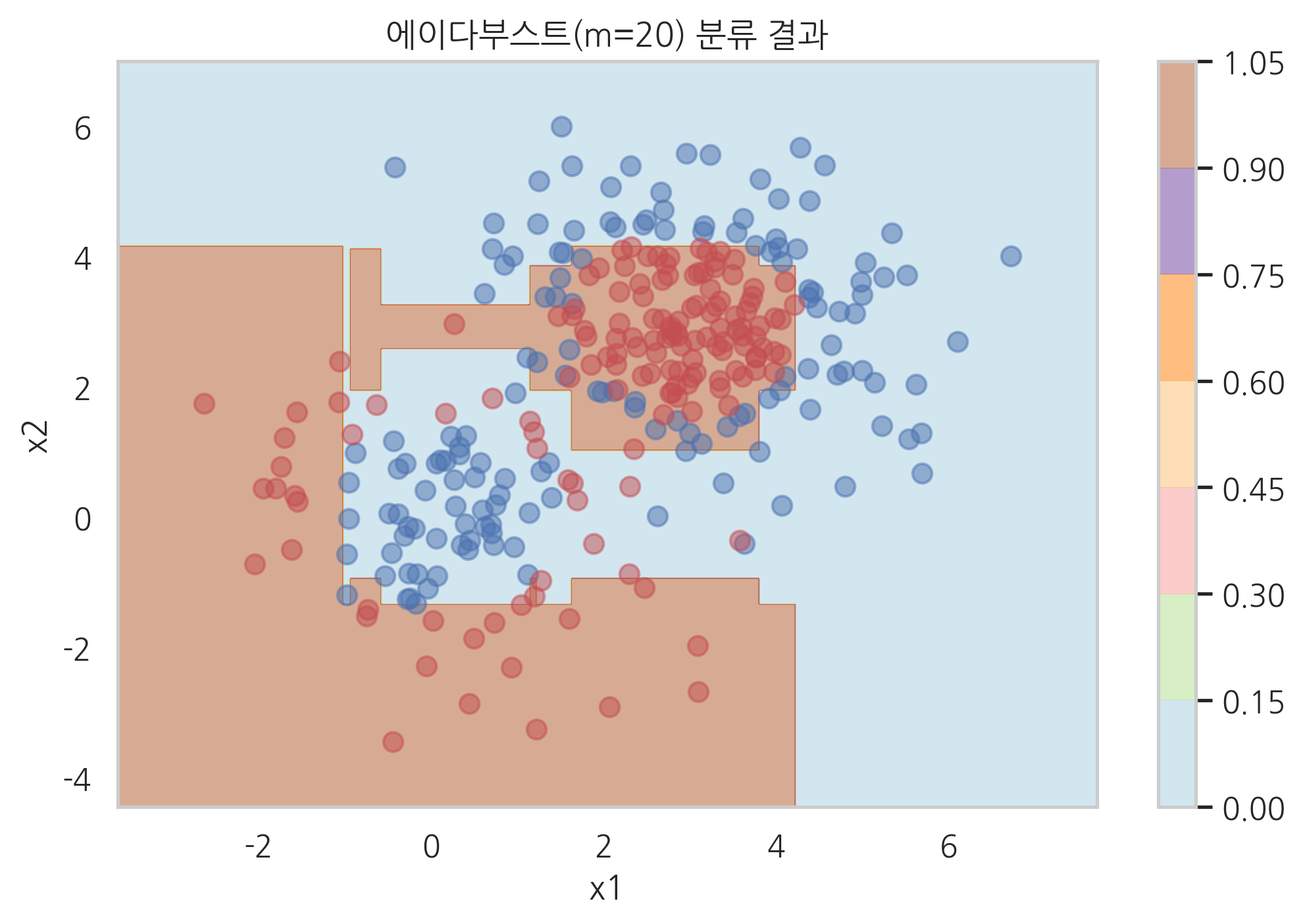
model_ada = MyAdaBoostClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1, random_state=0), n_estimators=20)
model_ada.fit(X, y)
def plot_result(model, title="분류결과", legend=False, s=50):
x1_min, x1_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1
x2_min, x2_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1
xx1, xx2 = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x1_min, x1_max, 0.02), np.arange(x2_min, x2_max, 0.02))
if isinstance(model, list):
Y = model[0].predict(np.c_[xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).reshape(xx1.shape)
for i in range(len(model) - 1):
Y += model[i + 1].predict(np.c_[xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).reshape(xx1.shape)
else:
Y = model.predict(np.c_[xx1.ravel(), xx2.ravel()]).reshape(xx1.shape)
cs = plt.contourf(xx1, xx2, Y, cmap=plt.cm.Paired, alpha=0.5)
for i, n, c in zip(range(2), "01", "br"):
idx = np.where(y == i)
plt.scatter(X[idx, 0], X[idx, 1], c=c, s=s, alpha=0.5, label="Class %s" % n)
plt.xlim(x1_min, x1_max)
plt.ylim(x2_min, x2_max)
plt.xlabel('x1')
plt.ylabel('x2')
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar(cs)
if legend:
plt.legend()
plt.grid(False)
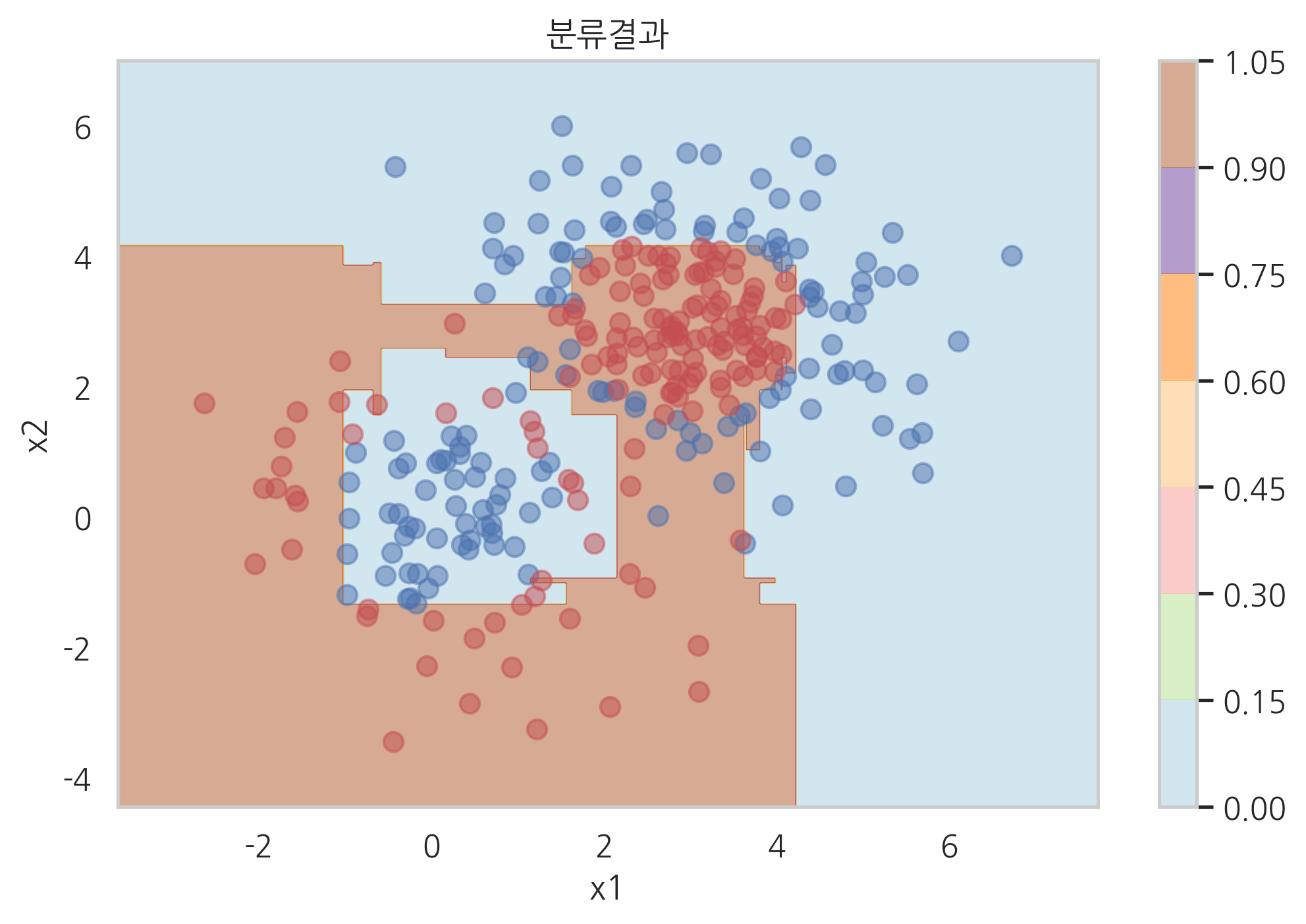
plot_result(model_ada, "에이다부스트(m=20) 분류 결과")
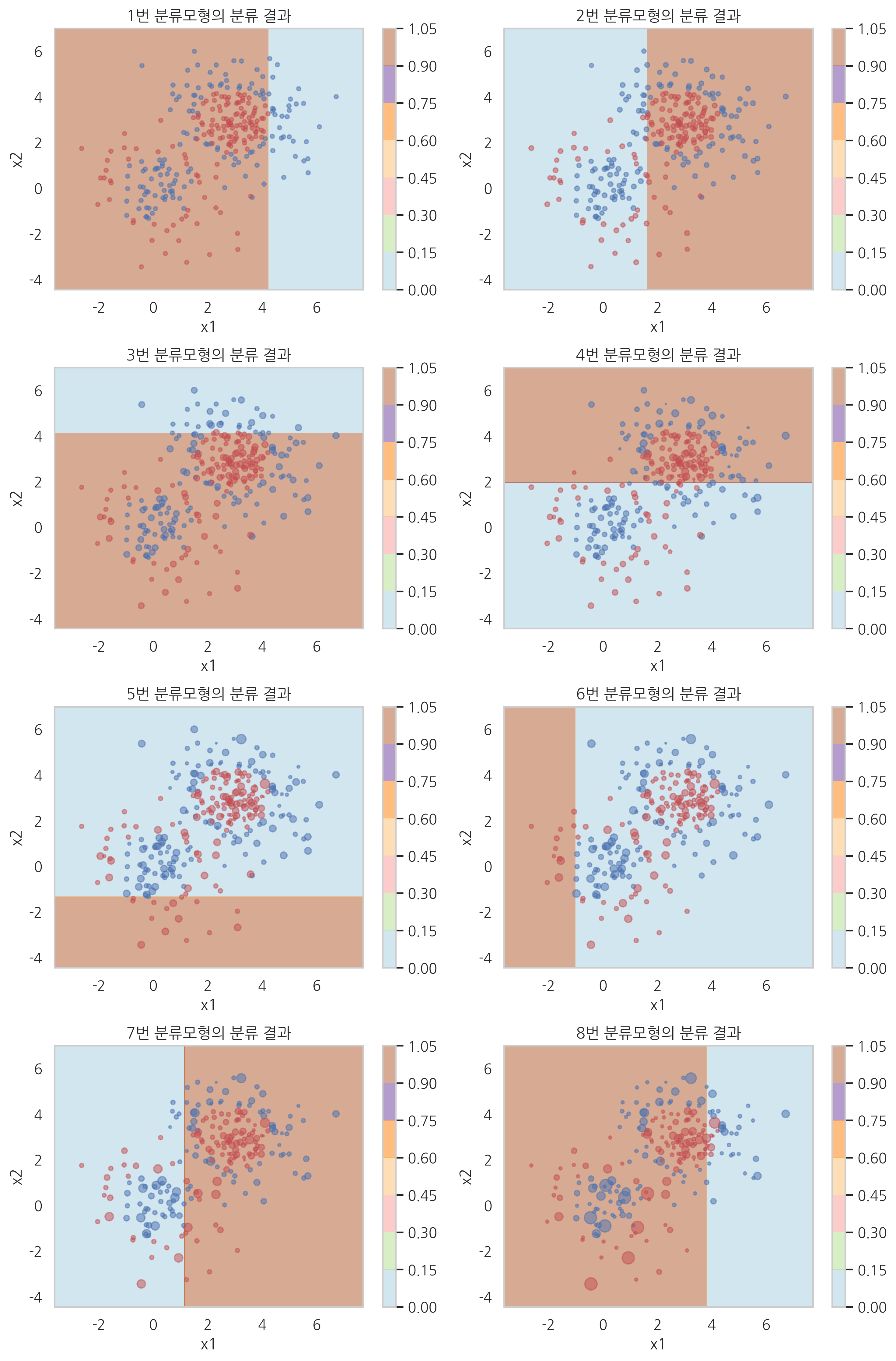
각 단계의 분류 모형에 대한 가중치 값과 분류 모형의 분류 결과를 시각화하면 다음과 같다. 데이터의 가중치는 스캐터플롯의 점의 크기로 표현하였다. 단계가 진행될 수록 가중치값의 변화가 커지는 것을 볼 수 있다.
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 15))
plt.subplot(421);
plot_result(model_ada.estimators_[0], "1번 분류모형의 분류 결과", s=10)
plt.subplot(422);
plot_result(model_ada.estimators_[1], "2번 분류모형의 분류 결과", s=(4000*model_ada.sample_weight[0]).astype(int))
plt.subplot(423);
plot_result(model_ada.estimators_[2], "3번 분류모형의 분류 결과", s=(4000*model_ada.sample_weight[1]).astype(int))
plt.subplot(424);
plot_result(model_ada.estimators_[3], "4번 분류모형의 분류 결과", s=(4000*model_ada.sample_weight[2]).astype(int))
plt.subplot(425);
plot_result(model_ada.estimators_[4], "5번 분류모형의 분류 결과", s=(4000*model_ada.sample_weight[3]).astype(int))
plt.subplot(426);
plot_result(model_ada.estimators_[5], "6번 분류모형의 분류 결과", s=(4000*model_ada.sample_weight[4]).astype(int))
plt.subplot(427);
plot_result(model_ada.estimators_[6], "7번 분류모형의 분류 결과", s=(4000*model_ada.sample_weight[5]).astype(int))
plt.subplot(428);
plot_result(model_ada.estimators_[7], "8번 분류모형의 분류 결과", s=(4000*model_ada.sample_weight[6]).astype(int))
plt.tight_layout()
에이다부스트 모형의 정규화#
에이다부스트 모형이 과최적화가 되는 경우에는 학습 속도(learning rate) 조정하여 정규화를 할 수 있다. 이는 필요한 멤버의 수를 강제로 증가시켜서 과최적화를 막는 역할을 한다.
AdaBoostClassifier 클래스에서는 learning_rate 인수를 1보다 적게 주면 새로운 멤버의 가중치를 강제로 낮춘다.
연습 문제 1#
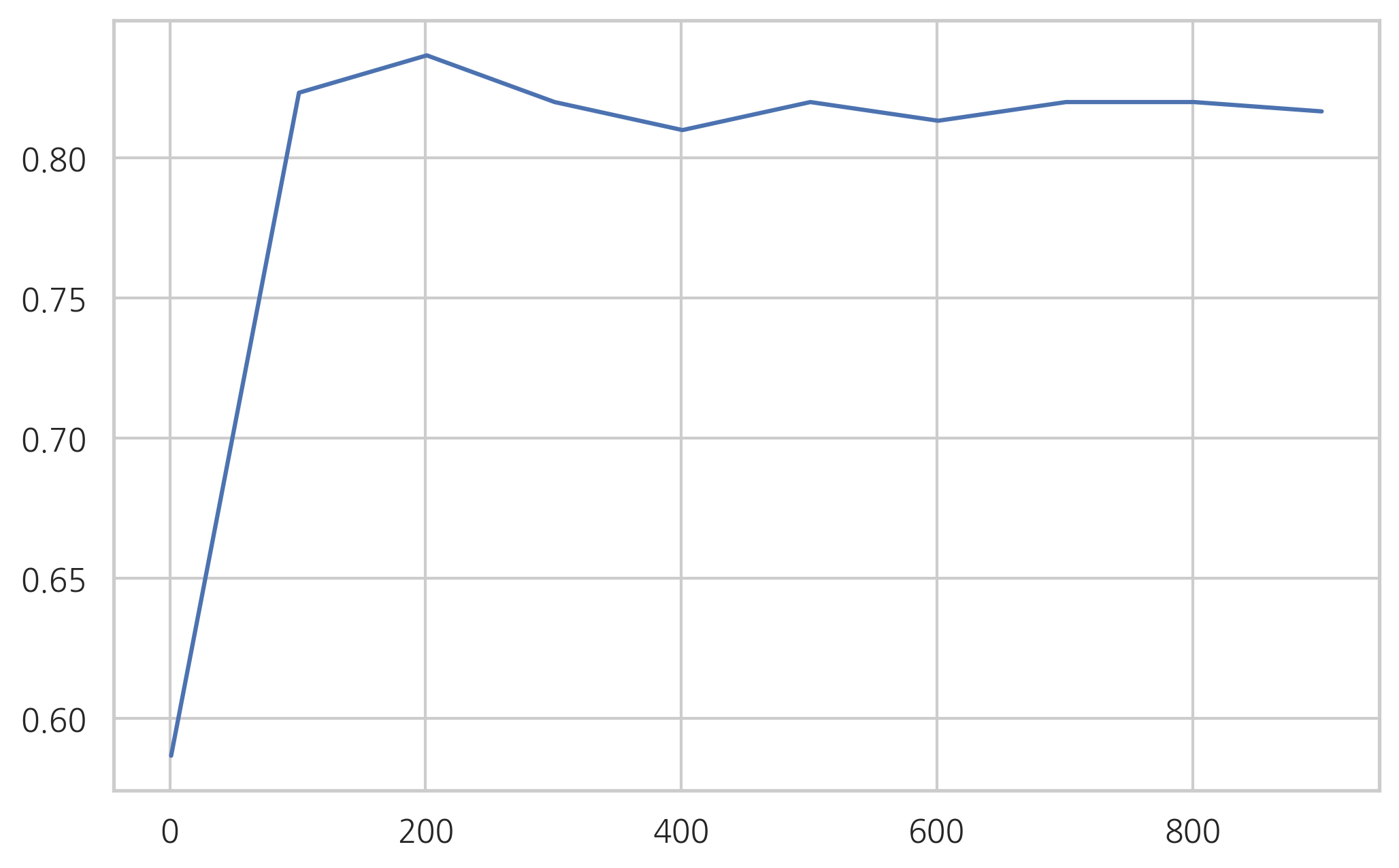
위 예제에서 멤버의 수를 1000까지 100단위로 증가시키면서 성능의 변화를 살펴본다. 과최적화가 심해지는가 감소하는가?
멤버의 수가 1000일 때 학습속도(
learning_rate)인수를 조정하여 과최적화를 없애본다. K=5인 교차검정을 이용하여 가장 검증성능이 좋은 학습속도를 찾아라.
%%time
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
mean_test_accuracy = []
for n in np.arange(1, 1001, 100):
model1 = AdaBoostClassifier(DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1), n_estimators=n)
mean_test_accuracy.append(cross_val_score(model1, X, y, cv=5).mean())
CPU times: user 2min 1s, sys: 1.62 s, total: 2min 2s
Wall time: 2min 4s
plt.plot(np.arange(1, 1000, 100), mean_test_accuracy)
plt.show()
그레디언트 부스트#
그레이던트 부스트 모형은 변분법(calculus of variations)을 사용한 모형이다.
함수 \(f(x)\)를 최소화하는 \(x\)는 다음과 같이 gradient descent 방법으로 찾을 수 있다.
그레디언트 부스트 모형에서는 손실 범함수(loss functional) \(L(y, C_{m-1})\)을 최소화하는 개별 분류함수 \(k_m\)를 찾는다. 이론적으로 가장 최적의 함수는 범함수의 미분이다.
따라서 그레디언트 부스트 모형은 분류/회귀 문제에 상관없이 개별 멤버 모형으로 회귀분석 모형을 사용한다. 가장 많이 사용되는 회귀분석 모형은 의사결정 회귀나무(decision tree regression model) 모형이다.
그레디언트 부스트 모형에서는 다음과 같은 과정을 반복하여 멤버와 그 가중치를 계산한다.
\(-\tfrac{\delta L(y, C_m)}{\delta C_m}\) 를 목표값으로 개별 멤버 모형 \(k_m\) 을 찾는다.
\( \left( y - (C_{m-1} + \alpha_m k_m) \right)^2 \) 를 최소화하는 스텝사이즈 \(\alpha_m\) 을 찾는다.
\(C_m = C_{m-1} + \alpha_m k_m\) 최종 모형을 갱신한다.
만약 손실 범함수가 오차 제곱 형태라면
범함수의 미분은 실제 목푯값 \(y\)와 \(C_{m-1}\)과의 차이 즉, 잔차(residual)가 된다.
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
model_grad = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=2, random_state=0)
%%time
model_grad.fit(X, y)
CPU times: user 50 ms, sys: 0 ns, total: 50 ms
Wall time: 50.4 ms
GradientBoostingClassifier(criterion='friedman_mse', init=None,
learning_rate=0.1, loss='deviance', max_depth=2,
max_features=None, max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=100,
n_iter_no_change=None, presort='auto',
random_state=0, subsample=1.0, tol=0.0001,
validation_fraction=0.1, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
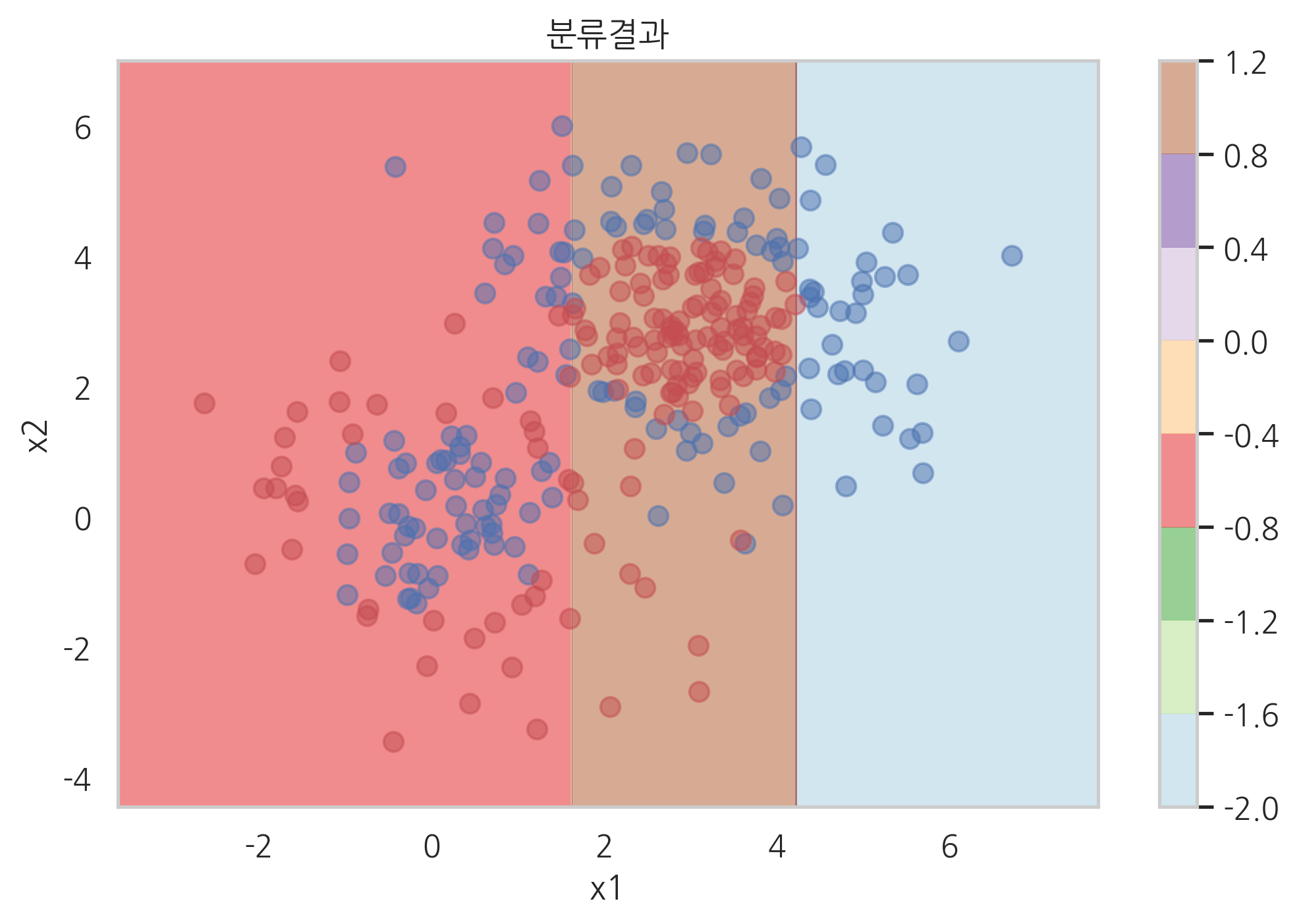
plot_result(model_grad)
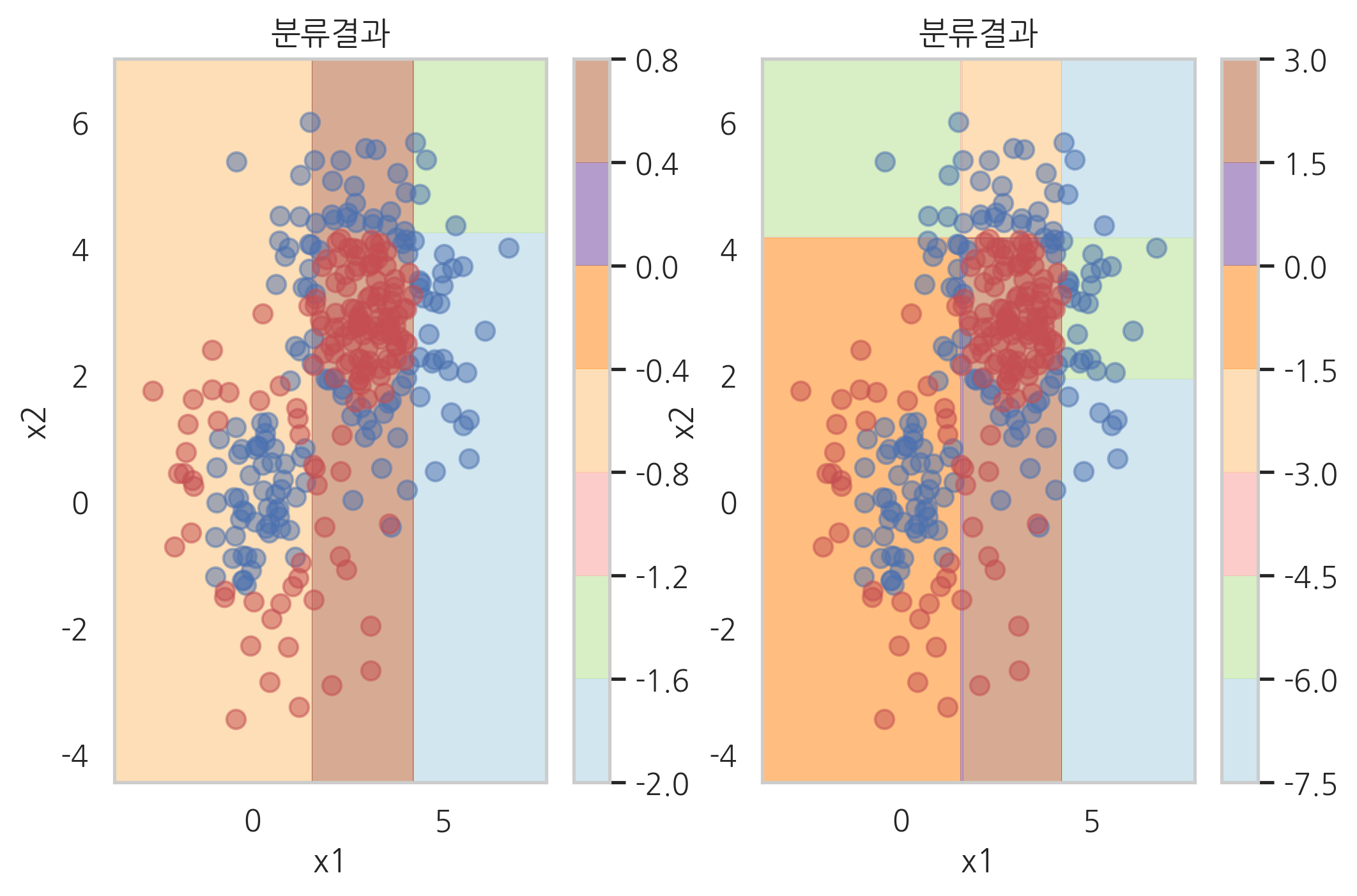
plot_result(model_grad.estimators_[0][0])
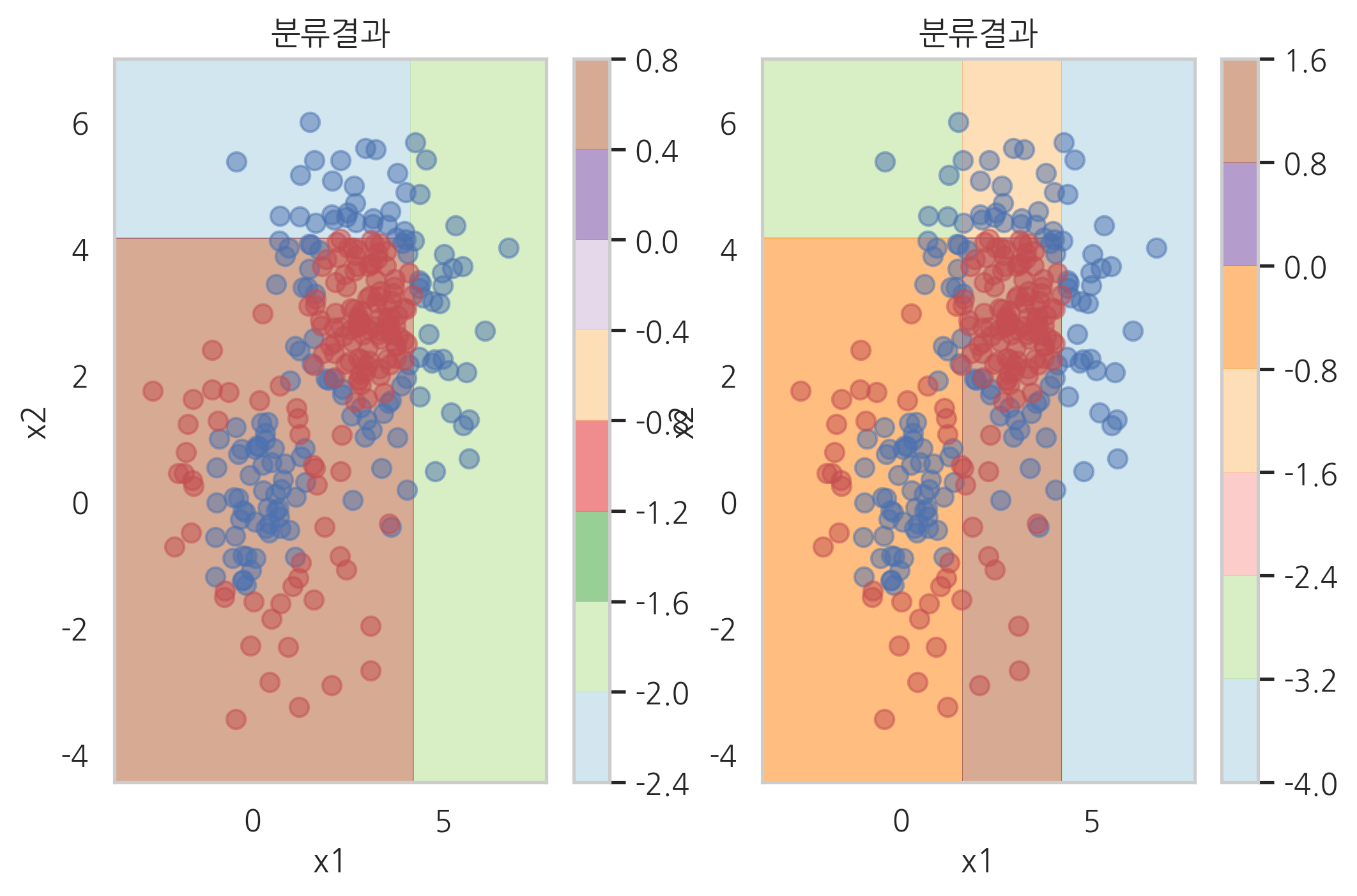
plt.subplot(121)
plot_result(model_grad.estimators_[1][0])
plt.subplot(122)
plot_result([model_grad.estimators_[0][0], model_grad.estimators_[1][0]])
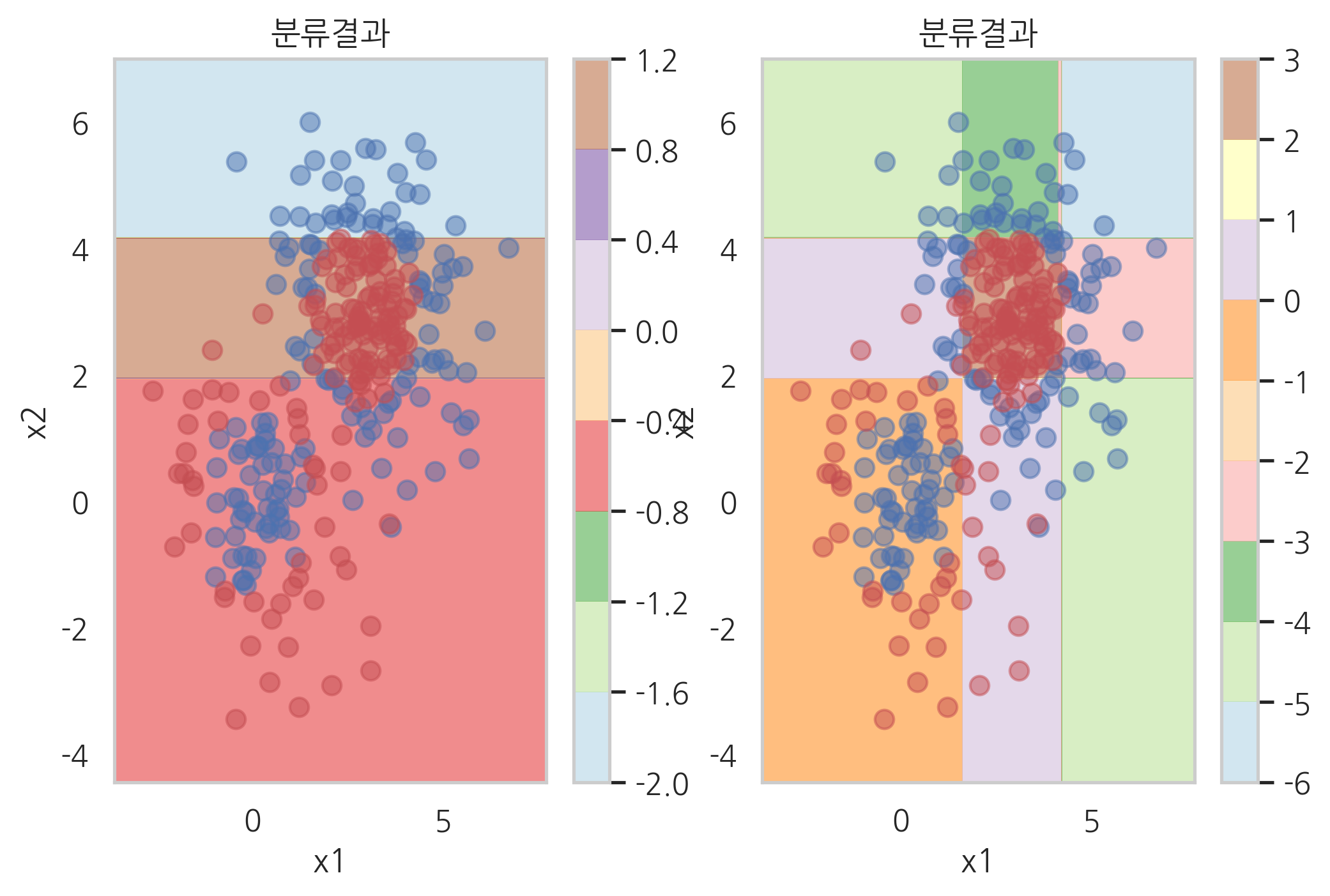
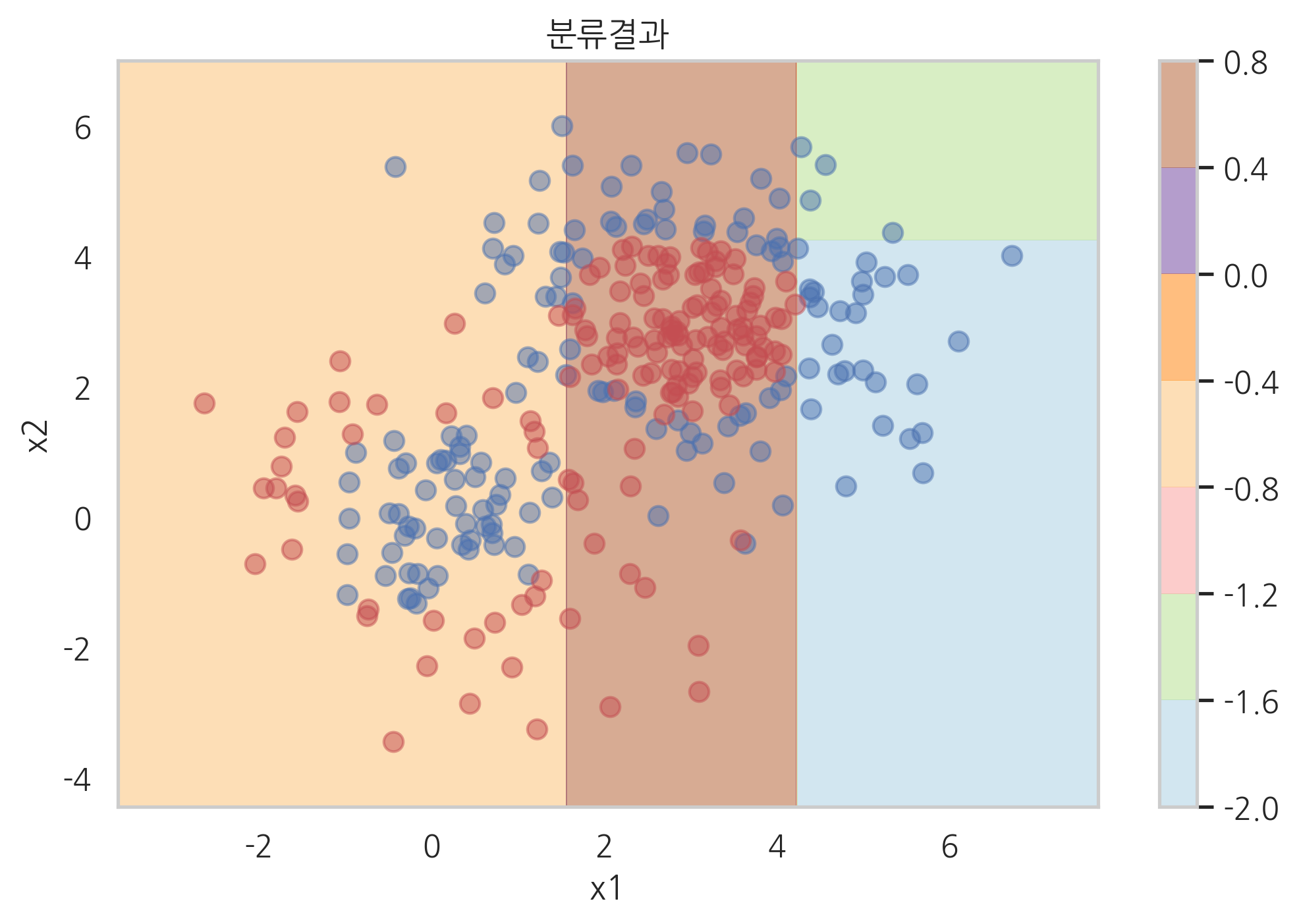
plt.subplot(121)
plot_result(model_grad.estimators_[2][0])
plt.subplot(122)
plot_result([model_grad.estimators_[0][0],
model_grad.estimators_[1][0],
model_grad.estimators_[2][0]])
plt.subplot(121)
plot_result(model_grad.estimators_[3][0])
plt.subplot(122)
plot_result([model_grad.estimators_[0][0],
model_grad.estimators_[1][0],
model_grad.estimators_[2][0],
model_grad.estimators_[3][0]])
plot_result(model_grad.estimators_[3][0])
XGBoost 라이브러리#
import xgboost
model_xgb = xgboost.XGBClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=1, random_state=0)
%%time
model_xgb.fit(X, y)
CPU times: user 20 ms, sys: 0 ns, total: 20 ms
Wall time: 12.2 ms
XGBClassifier(base_score=0.5, booster='gbtree', colsample_bylevel=1,
colsample_bynode=1, colsample_bytree=1, gamma=0,
learning_rate=0.1, max_delta_step=0, max_depth=1,
min_child_weight=1, missing=None, n_estimators=100, n_jobs=1,
nthread=None, objective='binary:logistic', random_state=0,
reg_alpha=0, reg_lambda=1, scale_pos_weight=1, seed=None,
silent=None, subsample=1, verbosity=1)
plot_result(model_xgb)
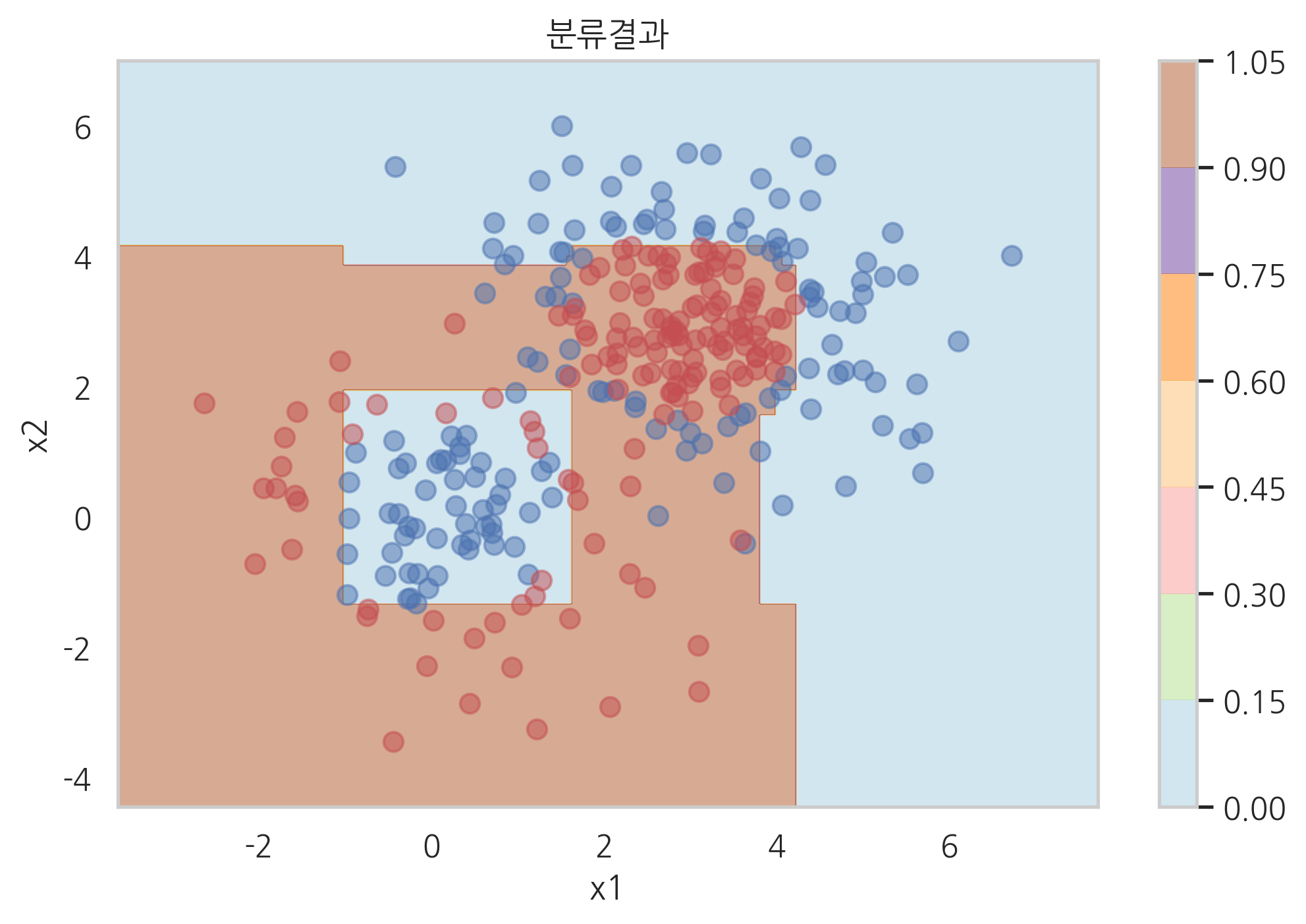
LightGBM 라이브러리#
import lightgbm
model_lgbm = lightgbm.LGBMClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=1, random_state=0)
%%time
model_lgbm.fit(X, y)
CPU times: user 10 ms, sys: 0 ns, total: 10 ms
Wall time: 15 ms
LGBMClassifier(boosting_type='gbdt', class_weight=None, colsample_bytree=1.0,
importance_type='split', learning_rate=0.1, max_depth=1,
min_child_samples=20, min_child_weight=0.001, min_split_gain=0.0,
n_estimators=100, n_jobs=-1, num_leaves=31, objective=None,
random_state=0, reg_alpha=0.0, reg_lambda=0.0, silent=True,
subsample=1.0, subsample_for_bin=200000, subsample_freq=0)
plot_result(model_lgbm)
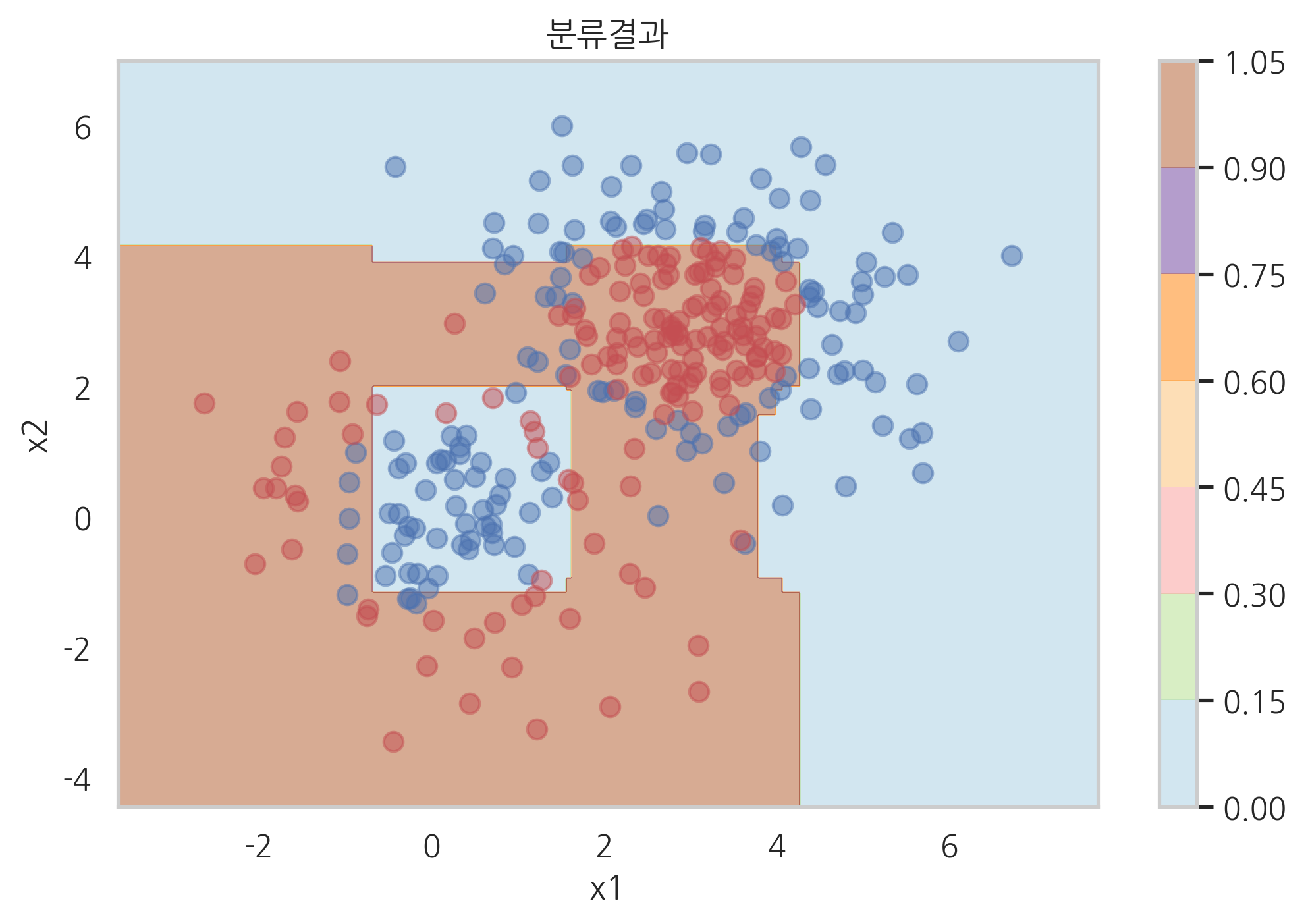
## 연습문제 1
model = AdaBoostClassifier(
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1, random_state=0),
n_estimators=200, learning_rate=0.1).fit(X, y)
plot_result(model, "에이다부스트 분류 결과")